Appearance
Confirmation
When a user orders a spicy sandwich, they may specify a level of spiciness that could be too intense for some people. To prevent discomfort, a bot might confirm if the user actually desires the requested spiciness level.
json
Chatbot: "How spicy do you want for your Tofu sandwich? On scale of 1 to 5?"
User: "5 please?"
Chatbot: "We use strong Jalapeño, so level 5 is considered deadly, are you sure you want level 5?"Overview
Even when a user's choice for a slot passes the value check, the business may still feel that there are things that the user might not know. As a result, the bot can inform the user of something through implicit confirmation or ask the user to confirm their choice through explicit confirmation.
To control this behavior, you can do the following:
- Decide which types of confirmation to use: explicit and implicit.
- Specify a conditional statement that triggers the confirmations.
- Support multi-valued slot confirmation via per-value confirmation.
- Provide corrections on the default and interruption strategies.
- Allow for customization of the "yes/no" understanding of user utterances under this context for explicit confirmations."
How to use
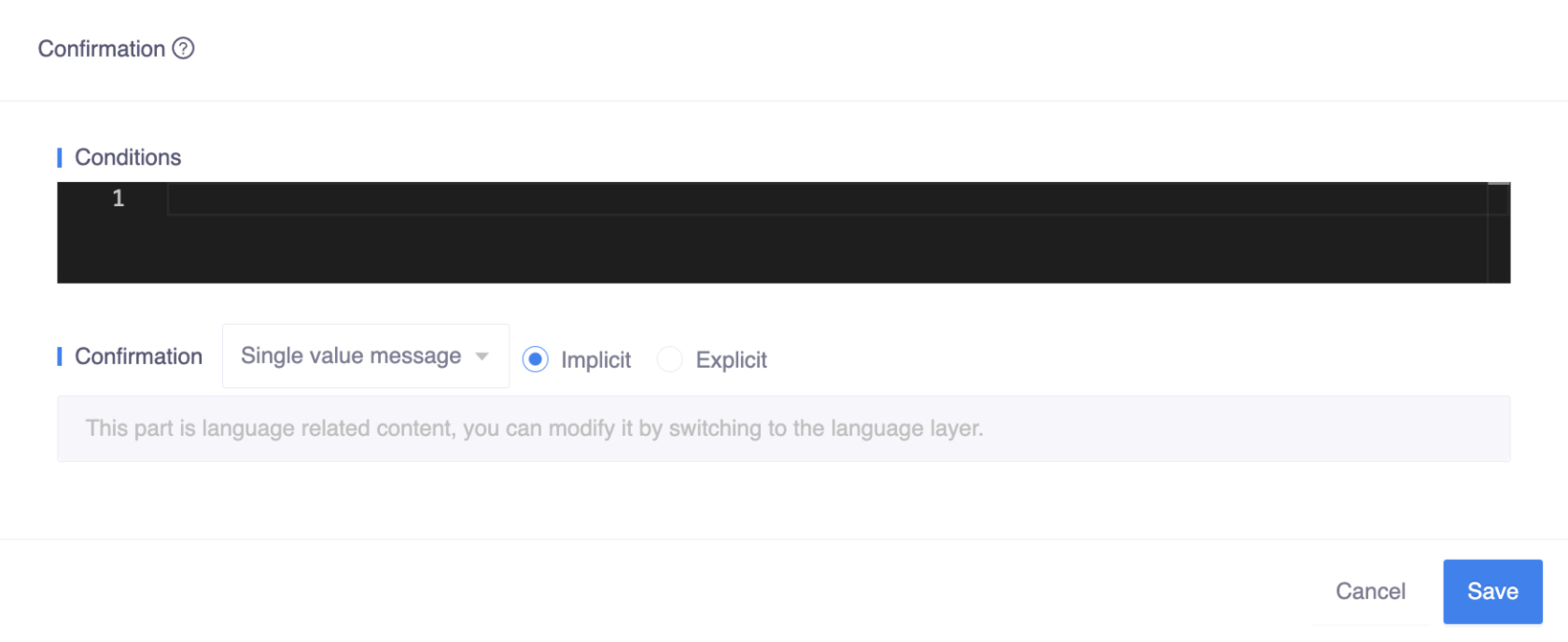
Confirmation is an optional annotation that can be defined at two different levels: slot level and type level, each with its own meaning:
- Slot level: The bot will confirm each slot that is defined.
- Type level: The bot will confirm after all slots on the frame/skill have been completed, bundling slots together for confirmation. Users can accept and modify batch confirmations.
Conditions
Using conditions, the bot can confirm with the user when a set of conditions is met. Kotlin code expressions can be used to specify the timing of key pieces of information that should be implied or requested.
json
User: "Get me two tickets for Adele on Jul 1st."
Chatbot: "Adele on Jul 1st, the Event Organizer is requiring all attendees to have been fully vaccinated (14 days past final vaccination show) AND to have received a negative COVID-19 test within 48 hours of the event. Please confirm you want to continue?"
User: "confirm"
Chatbot: "Please select your seats"In the example above, the bot will confirm the COVID-19 information and request a yes or no answer only when the artist is Adele. For other artists, this confirmation will not be triggered.
json
User: "Get me two tickets for Coldplay on Aug 16th."
Chatbot: "Coldplay on Aug 16th, please select your seats."In this case, there are multiple conditions that need to be set here:
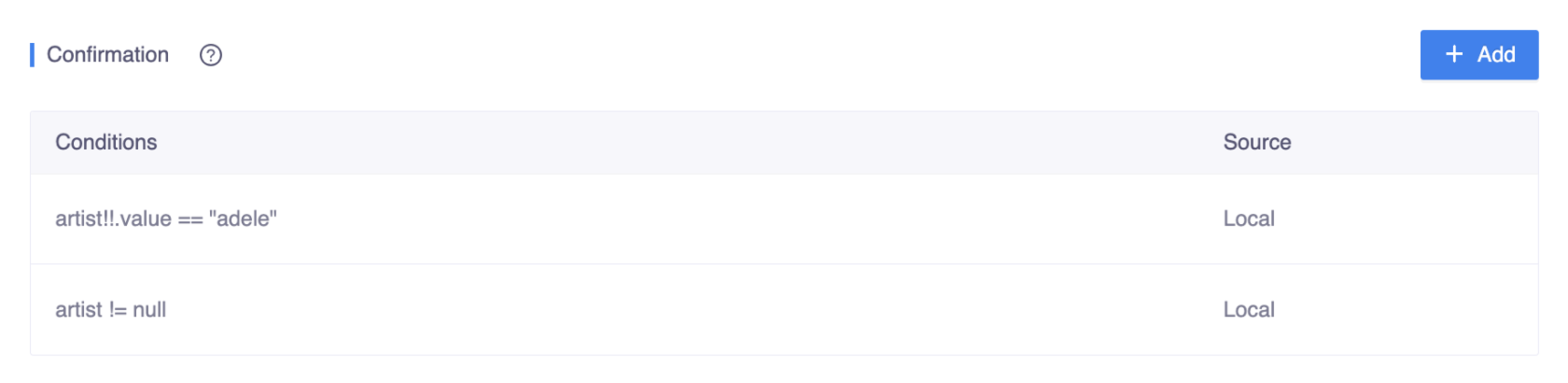
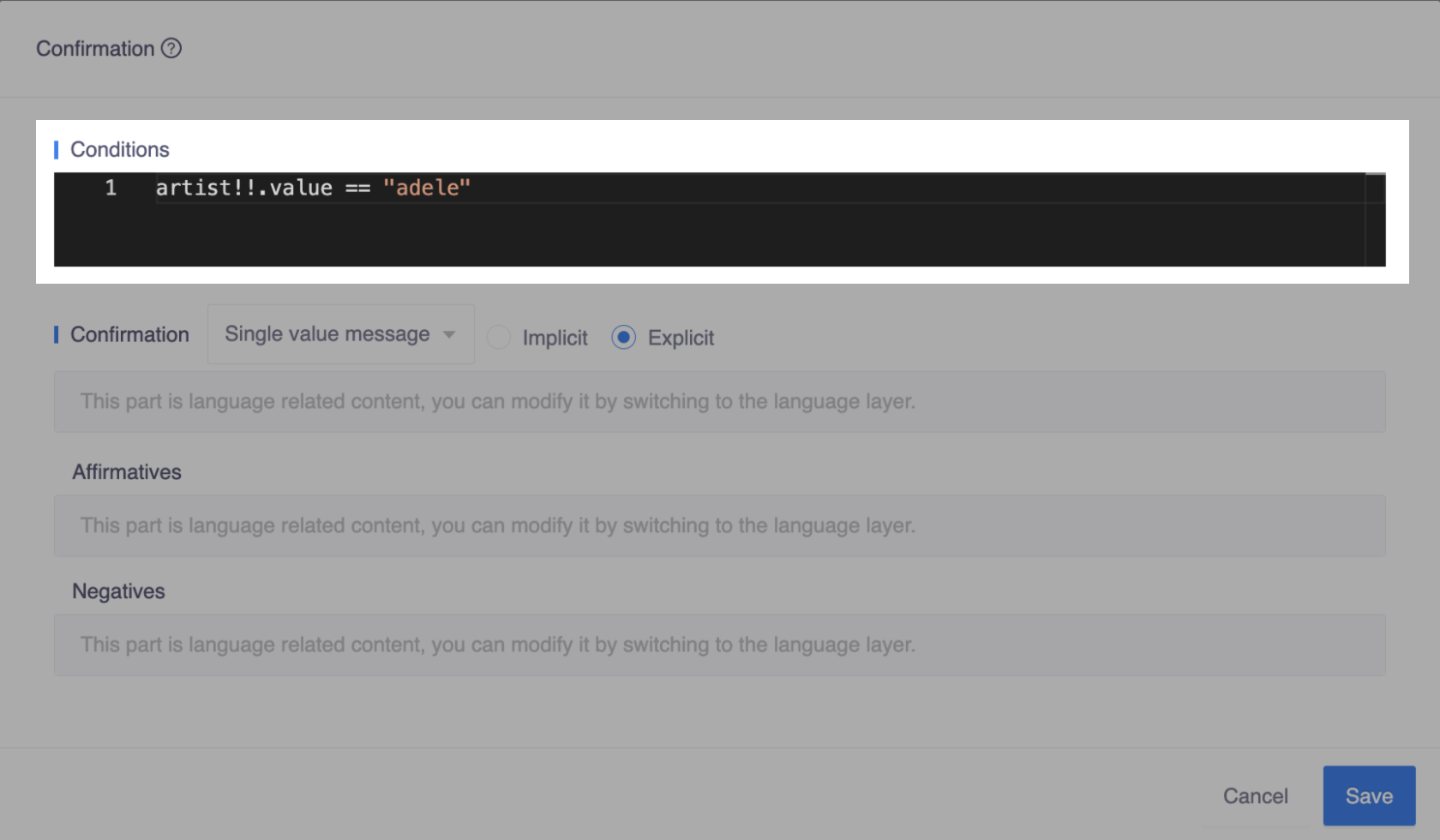
- One should be like
artist!!.value == "adele"orartist == Artist("adele"):
- Another can be simple, like
artist != null:
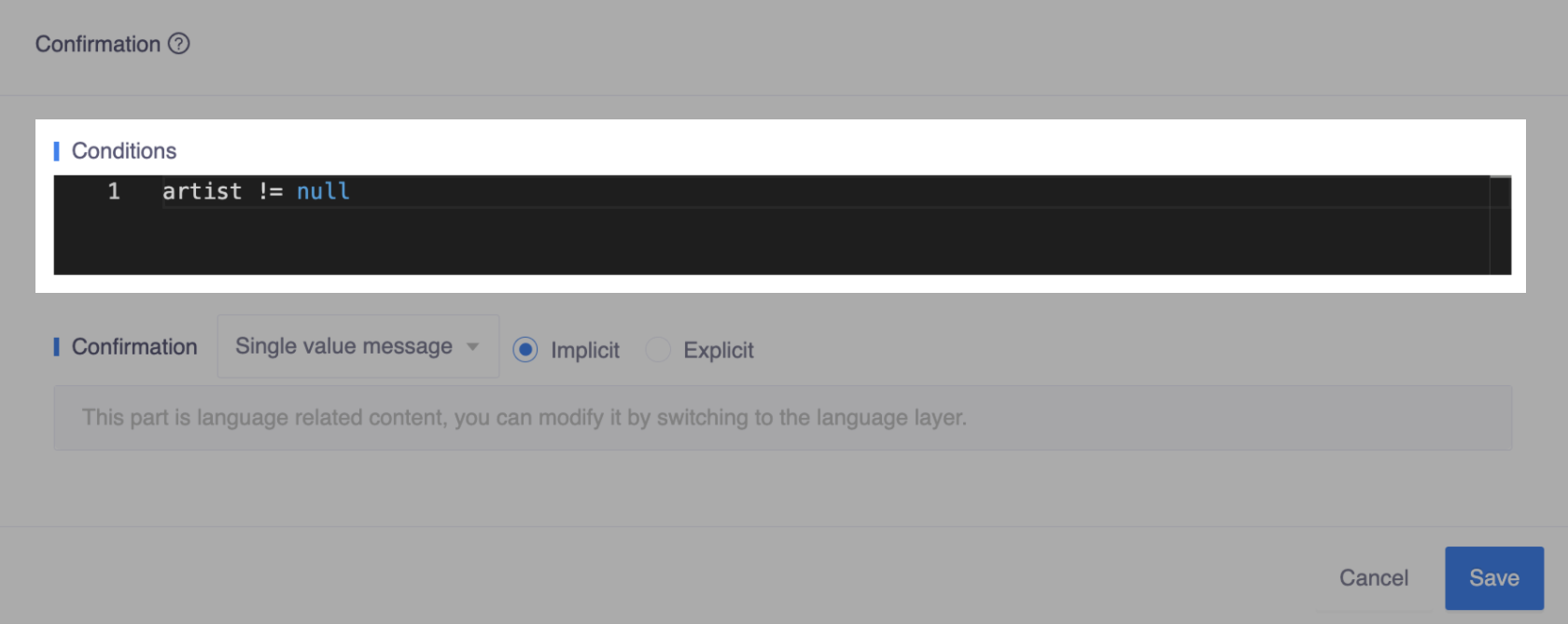
Bot will check the conditions according to the top-to-bottom order, and ask user for confirmation when the condition is met:
- If the first condition is
true, bot will respond the confirmation to the user. - if the first condition is
false, bot will move on to the next condition, and so on.
Explicit
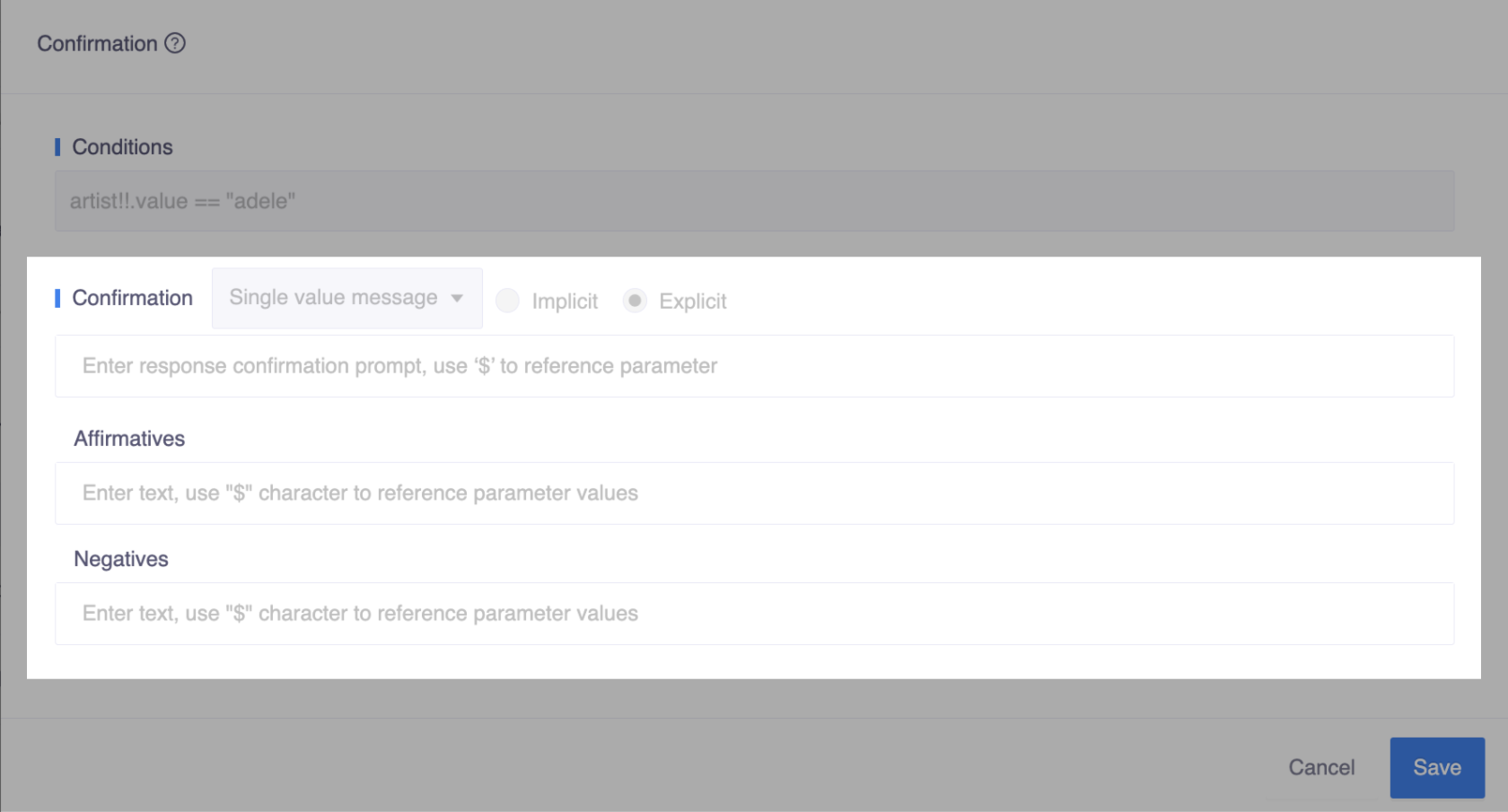
Explicit confirmation involves checking with the user that their input or request was understood correctly. It is often used to confirm critical details, and the bot will not perform the action until it receives a reply from the user, usually in the form of a yes/no or similar response.
For example, you can double-check with the user before performing an action that would be difficult to undo, such as canceling an order.
json
User: "Can I cancel an order?"
Chatbot: "Sure. Could you provide me with the order number?"
User: "123456"
Chatbot: "I found the order: [order details] Should I go ahead and Cancel the order?"
User: "Yes."
Chatbot: "I have cancelled the order for you. "But there are many ways to say yes or no by the user. To handle the synonym expressions of "yes/no", Affirmatives and Negatives provide the way for you to customize the "yes/no" understanding in specific contexts.
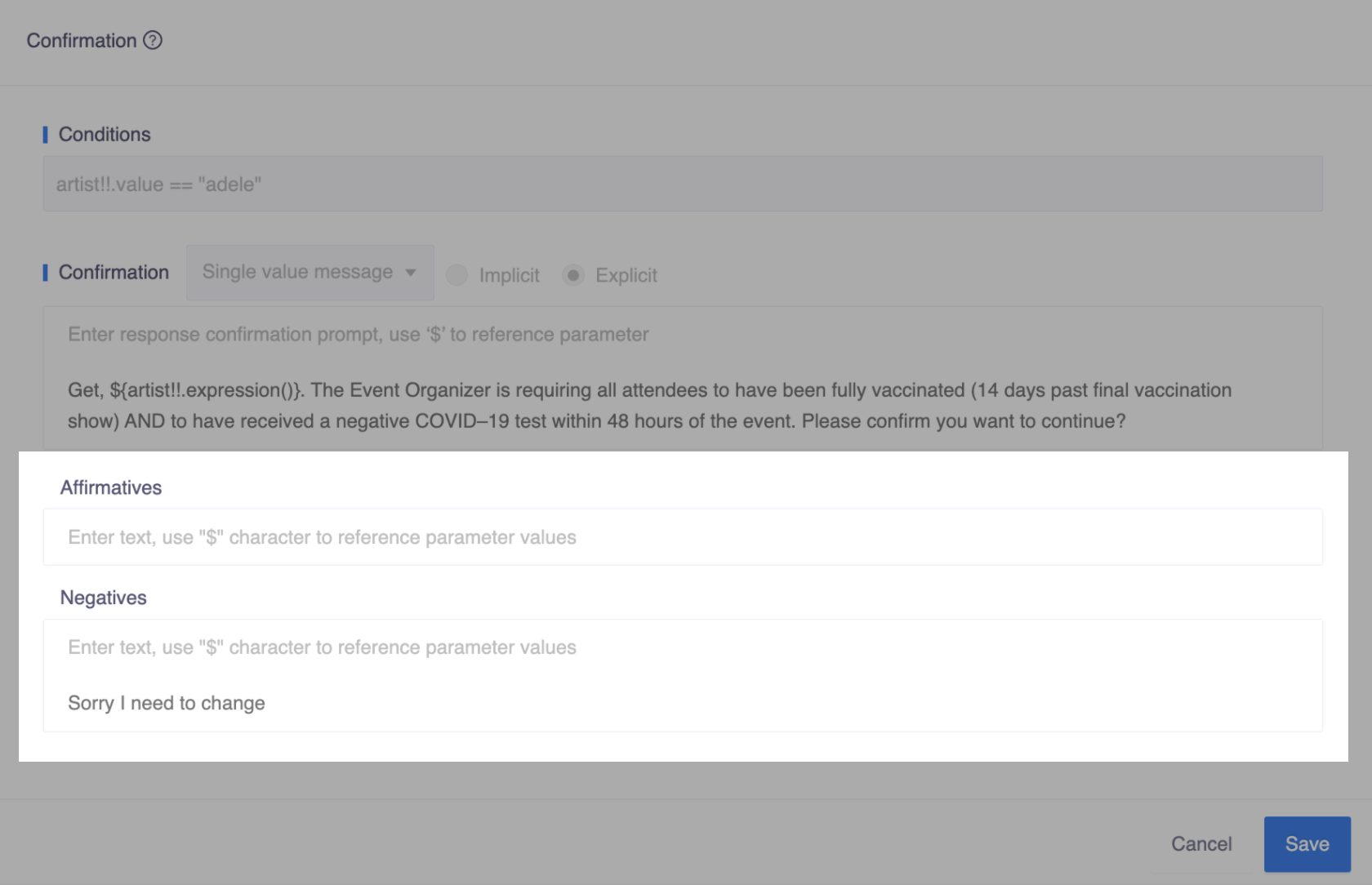
For instance, the phrase "Sorry I need to change" may imply a new intention in some situations, but it may signify a negative response to confirmation in other contexts. By defining all possible cases in Affirmatives and Negatives, the bot can better understand user responses and provide appropriate actions.
Note
The common understanding of confirmation yes and no is already supported in system skill io.opencui.core.confirmation.Yes and io.opencui.core.confirmation.No, so no need to define it here. But if needed, you can also customize system skill behavior by adding expressions.
Implicit
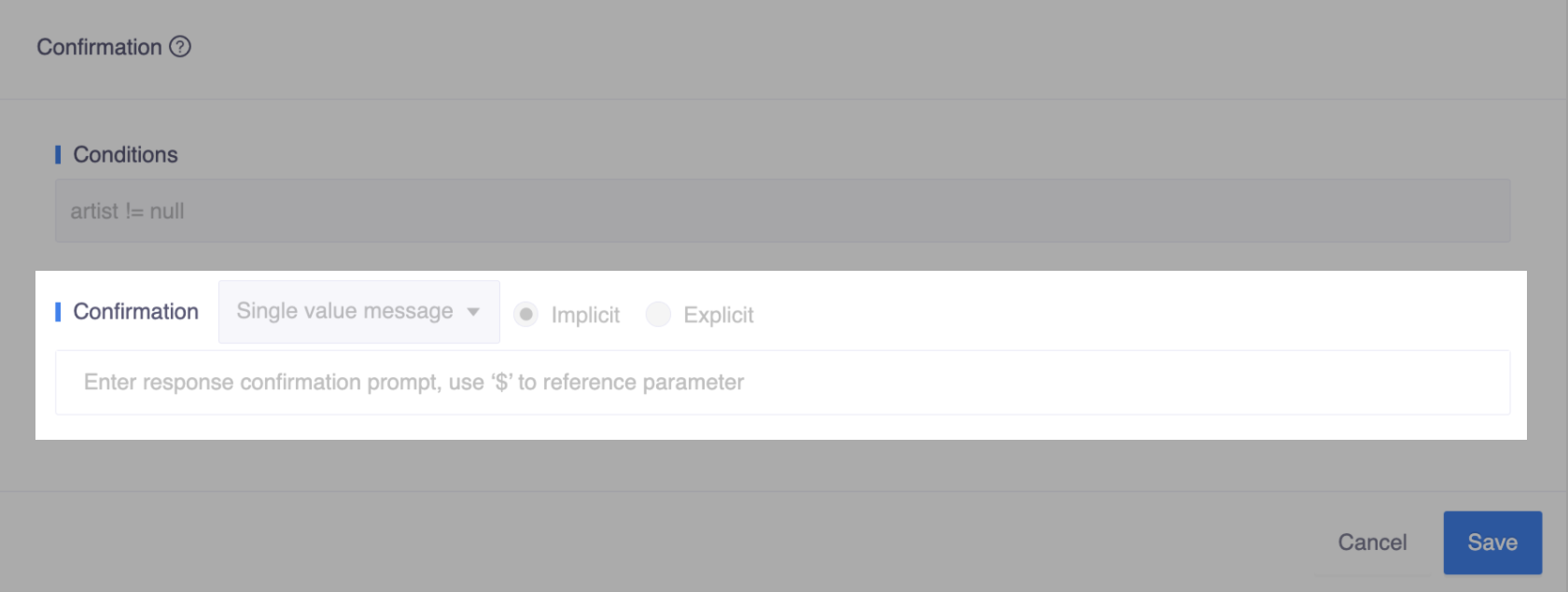
Unlike explicit confirmation, implicit confirmation does not require a reply from the user. It simply confirms that the input has been received as an FYI notification and an operation will take place without asking for user approval. Although users might give feedback if they want to make a correction.
json
User: "I need to change the shipping address."
Chatbot: "Can I get your street address?"
User: "[address]"
Chatbot: "Get. I will set your street address to be [address]. You will receive an email confirmation of this change in a few minutes. What else can I help you with?" OpenCUI
OpenCUI